Big data analysis is the next innovative technique that the telecommunications (telecom) sector is deploying. Big data will tame the telecommunications abundance of data, and enable harvesting information “gold” from existing data storage. We know that Big data includes paper as well as innovating new ways of collecting numerous touch-points of data.
Telecoms have always created and analyzed vast quantities of data about their customers — both financial and administrative transactions and operations. Telecom service providers have always been early adopters of data-related technologies. Included in this tech are old-school statistical analysis followed by data mining, knowledge management, and business intelligence applications.
According to a MindCommerce study:
“An average telecom operator generates billions of records per day, and data should be analyzed in real or near real-time to gain maximum benefit.”
For communications service providers (CSPs) to make use of insightful knowledge, much of the data must be processed in near real-time. Traditional systems would take days, weeks, even months to process the data, not to mention the complex variety of structured and unstructured data that would trip up legacy applications.
Big data analysis is used by telecommunications service providers (telecoms) in a variety of intriguing and practical ways that even a few years ago would not have been possible.
- CSPs monitor network traffic to identify problems to make decisions that improve service and customer satisfaction. The CSP operational diagnostic information also helps prioritize investment in the networks’ physical and technical assets.
- Telecoms analyze the metadata of call records to pinpoint fraudulent activities that protect their customers and criminal investigations.
- Telecoms index mountains of documents, images, and manuals within minutes to help call center agents resolve customer issues. Agents can now quickly search for information previously locked away in paper. The paper resolution reduces the call handling time, thereby reducing labor costs. For commerce, these finable documents boost efficiency, which can increase both employee and customer satisfaction — and retention.
- CSPs evaluate usage patterns to help businesses create service plans that better suit their customers’ needs. When you take care of your customers, it cuts customers’ costs — and more importantly to telecom companies — it helps them predict and reduce churn.
- Telecom companies even use data pouring in from social media networks to optimize the content of, and investment in marketing campaigns on the fly.
Telecom big data sources include the obvious such as phone calls, emails, and multi-media messages. The telecom big data authority also extends to geo-spatial information, transaction metadata, social media usage, log data, file downloads, sensor data, and more.
History of Big Data
Until recently, the variety and velocity of data were vexing. Disparate data being created at rapidly increasing rates presented insurmountable storage, and processing dilemmas.
It may seem like big data is a recent scourge, but data recording and ciphering its value has been going on since 7000 B.C. The earliest modern 20th-century big data problems were US federal government projects.
If only Franklin Roosevelt had known that he was a pioneer in big data. Read more about these and other intriguing big data history facts.
But it would be the 21st century, in 2005, before Roger Mougalas from O’Reilly Media named the problem of managing and processing large sets of data. All of the data produced and gathered cannot be conquered using traditional business intelligence tools.
The term “big data” came long after the knowledge that there was a plethora of information that existed. And each year, each month and each day since, the amount of data have been recognized — innovations have been critical to contain it all.
The Internet of Things (IoT) drives the unfathomable speeds and quantity of data from sensors that are used for calculations. These calculations are lightning-quick, often life-preserving. By their very nature, these calculations must result in instant decisions and actions.
Telecom’s Big Data Analytics Trends
Some of the hyped-topics in telecom technology, such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), and even the latest 5G feel like it fizzles to many consumers. But the misunderstanding is mostly because of emerging innovations required to make the information happen. There is a latency between possibilities, and the human mind’s ability to take it all in.
All technology can’t be understood by the layperson, as raw material is presented for the next paradigm about-face. For sure, those technologies will deliver applications, both practical and entertaining, that will exponentially accelerate the creation of data. But for all persons to “get” or understand what is happening in the telecommunications field is like asking the community to understand a booster rocket. All people are not trained engineers, and they won’t have a firm grasp on the technical aspects.
For example, Kevin Westcott, Deloitte’s VP and leader of its US Telecom practice, predicts the popularity of e-sports to skyrocket. We all get that we want the popularity and reputation of e-sports to rise. But, this prediction was before the world-altering COVID-19 pandemic.
When you send millions of individuals into isolation — with little to do but seek out streamed entertainment — something will change in our world and the world of commerce. The forced isolation of the pandemic has brought cancellations of the entire seasons of the world’s hottest sports organizations. E-sports and the big data it generates will likely heat up faster than the predicted trends.
Also, legalized sports betting is on the rise following a 2018 US Supreme Court decision lifting the federal ban on sports betting.
To follow suit — several states have already legalized sports betting. 5G’s low-latency, high-volume communications will enable real-time sports betting. With 5G already being deployed in stadiums and sports bars, betting from your seat or barstool is imminent. (Yes, we are all hoping the stadiums and sports bars will be opened soon.)
Telecoms are at the ready — as they should be — to analyze every wager. New telecom connectivity technologies like 5G fixed wireless and satellite internet will offer the backbones needed for disruptive, big-data birthing applications.
The aggressive growth of smart homes and cars, video on demand, streaming apps, gaming, and other entertainment and educational applications will continue producing even higher volumes of data. The data will then be analyzed to glean the insights for businesses and other operational decisions.
Big Data Analytics Solutions
Big data analytics technologies are evolving right along with the technologies and supporting infrastructure. These are the very structures that created the formidable volumes of data in the first place. Companies must be able to collect data from different sources, analyze them, and distribute the information to disparate databases. Data centers or data warehouses are awaiting the intelligence, and depending on the data for the specific needs of the organization.
Marketing Campaigns
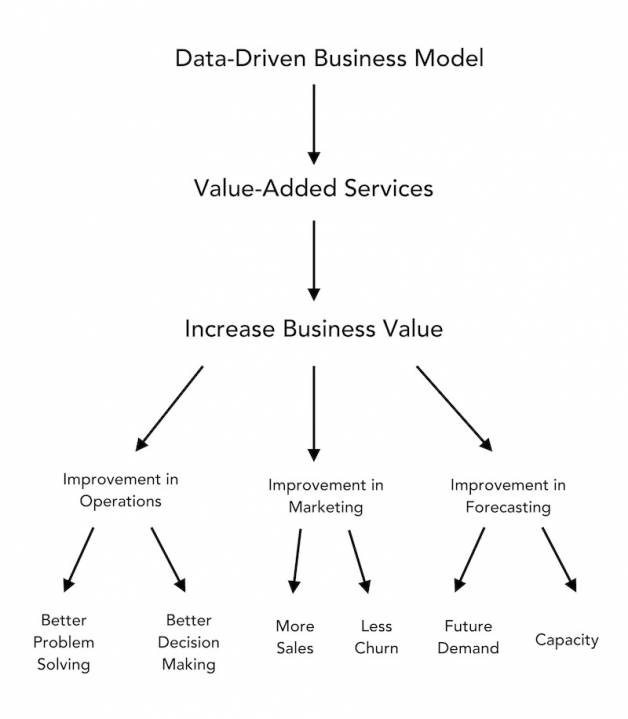
The challenge with big data projects is finding skilled resources with experience to create cutting-edge architectures and supersonic data processing applications. These data processing applications must support data-driven business models and near-real-time hyper-targeted marketing campaigns.
Problem-Solving Teams
Teams for solving big data problems must have a wide variety of engineers, analysts, business experts, and system integrators. These specialized teams are rarely found in-house for most companies, even large telecom service providers.
Outsourcing
Outsourcing and staff augmentation is frequently used for big data ventures. For example, Vates, a leading big data analytics and systems integration company in Latin America, is in the center of some of the biggest telecom big data projects in the world.
Global Telecom Company
Vates was hired by a global telecom company to bring its engineering and agile project management prowess to meld with the development of a system. Engineering teams located across the US, Chile, and Argentina are working on the development.
IBM Streaming Analytics
The combined in-house and outsourced team utilized IBM Streaming Analytics to develop architecture and big data analytics solutions. These processes take and analyze the unstructured and structured metadata from multiple sources in near-real-time.
One of the resulting systems was created using IBM Streams processes. The IBM system processes 35 million CSV files or 100 terabytes of data per month. You can read about these impressive big data analytics use cases for the Telecom company.
The Vates Expertise
In a follow-on project for the same telecom, Vates utilized its expertise. Vates works with data from different formats, that originate from varied locations. The company can create solutions capable of checking network quality (NQI) in near-real-time.
Receiving XML files with measurements as detailed as the antenna position, the company can calculate its deviations. The information enables the system to gauge signal quality at a particular location. With this microscopic big data, a technician can quickly make necessary corrections.
Patterns
The insight-sifting solutions uncover hidden patterns, trends, and profound perceptions of customer behavior. Within this data is other useful business, operational, and marketing information — all bringing instantaneous business value.
As big data technologies evolve, solutions will likely be developed by blended teams. These blended teams will be using outsourcing and staff augmentation to overcome the challenges of staying on the leading edge.