The rapid evolution of technology and data processing capabilities is paving the way for more advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools in Law firms. While there are tangible benefits associated with generating AI applications in various legal tasks, it must be done with a prudent approach to ensure responsible implementation and regulation adherence.
Generative AI tools evolved from highly advanced data processing provisions that enable formatively instructed computers to spotlight future and likely trends analogous to human-exhibited alternate ways of decision-making and pattern identification.
This blog reviews the compensations, and defenses, followed by points of caution before moving towards how foresighted strategies stand to advantage in efficiently managing appropriate Uses for Artificial Intelligence as applied in the Legal service territory.
Benefits and Challenges of Generative AI Tools
Advantages of using generative AI in legal practices
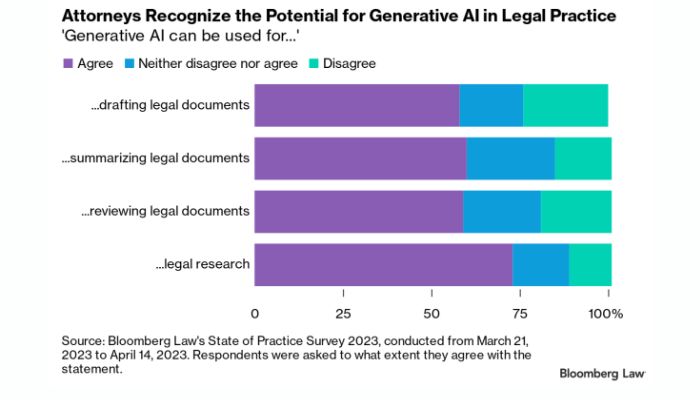
Generative AI tools — defined as AI algorithms that automatically generate, understand, manipulate and implement fixed-data input from real-world events- are proving valuable to legal professionals by enabling them to keep pace with vital developments.
Studies show that using generative AI in legal practice can significantly reduce costs associated with sifting through case law evidence and creating briefs, arbitration documents and expert opinions.
In addition, technology is socially advantageous by making the judicial system more accessible by generating natural language that’s better and faster for decisions rather than manual rulings.
Additionally, the predictive capabilities of such tools have enabled lawyers to obtain more insight into estimating odds of winning cases; something extremely useful for evaluating how cases should be viewed towards trial.
Potential risks and ethical considerations associated with AI implementation
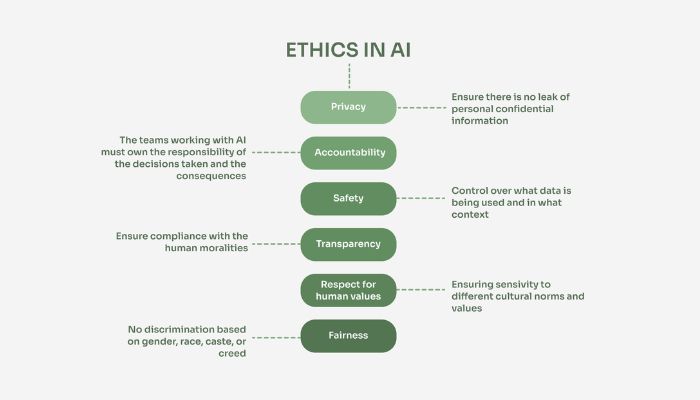
Generative AI tools offer great efficiency improvements in the legal field, but they can potentially introduce ethical considerations and risks. For one, AI-driven software can discriminate against certain minority categories inadvertently if the data used to build it contains biases. One concern is when low-quality or biased data sets are used to generate predictions or make decisions.
Furthermore, generative AI raises questions of privacy that lawyers must consider when transferring huge quantities of data retained needed by AI tools. In addition, malware and hacking efforts placed into artificial intelligence systems can target many protective aspects researched for lawyers’ benefit and those of their clients.
Thus, developers must pay special attention to cybersecurity threats posed by the implementation of artificial intelligence tools in legal practices.
Shift towards Cautious Approaches
Notable cases of AI-related errors or biases in the legal field
In recent years, there have been multiple notable cases of AI-related errors or biases in the legal field.
Notably, consumers were led astray by an algorithmically generated predictive guide specifying their criminal representation rights which charged them as must-choose fees after promising free services.
Moreover, an AI system used to determine risk levels of prisoners was proved bias towards people who are African American leading to unequal opportunities available to them while hearing sentencing outcomes.
Awareness of potential pitfalls leading to a cautious mindset
Law firms have started realizing the need for cautious implementation of generative AI tools in order to avoid errors and comply with regulatory frameworks. Instances of mistakes and biases related to AI usage in the legal quarters have reminded them about the long-term consequences that AI can leave upon them for unaccounted risk exposure.
As a result, law firms are increasingly adopting a hunker-down skepticism which means approaching future implementations and the whole process of testing with much rigor and diligence in order to mitigate potential liabilities.
This more careful strategy gives them an advantage as it eliminates possible errors from emerging trends, helps concentrate resources on meaningful use cases along with unlocking long-term effects due to process improvement.
Factors Influencing Cautious Adoption
Regulatory concerns and compliance issues
The legal field is highly regulated, and there is uncertainty surrounding the scope of regulatory oversight when AI tools are implemented. Compliance issues can pose risks in terms of liability and breach of laws or regulations.
Implementing AI often means moving or transferring information from a physical to an electronic format — which raises data protection compliance risks due to difficulties ensuring confidentiality agreements or assessment of privacy risks associated with data processing.
Uncertainty about AI’s long-term impact on legal practice
There is still a degree of uncertainty regarding the full potential of Artificial Intelligence to disrupt key aspects of legal practice. With no proven models on AI ethics yet in place, many firms are thus taking a cautious approach to preventing any surprises down the line.
Questions have also arisen from experts and practitioners in related fields about how AI may impact employment opportunities within legal spheres and regulators alike have begun developing specific policies on generative AI development, all adding fuel to anticipation.
Above all, the need for diligence as technology evolves has led fearlessly innovative law firms to push for careful strategizing when it comes to procedural use and implementation.
Implementing Prudent Strategies
Conducting thorough AI tool evaluations and testing
Law firms are recognizing the importance of conducting thorough evaluations prior to implementing generative AI tools.
Such tests help identify legal risks that need to be addressed in the technology, including delineating how it makes decisions and defending its data management processes, key factors towards considering whether the software is fit for usae.
Firms also assess practical considerations which that can aid integration with existing IT systems and future scalability.
By testing AI tool capabilities and potential pitfalls, law firms are prioritizing risk mitigation over instant gratification about being early adopters of innovative legal tech.
Training legal professionals on AI ethics and responsible use
In order to ensure that AI technology is implemented in the most responsible way on behalf of law firms, prudent strategies need to be adopted.
One such measure involves training legal professionals on not only the efficiency and clinical aspects of the new AI tools but also ensuring that they are well-informed on ethical codes and regulations regarding AI utilization for safety.
Well-trained professionals in conjunction with customized solutions from collaborators provide an entry point into wider adoption without taking unnecessary risks.
Collaboration with AI Developers
Working closely with AI developers to address concerns
Collaboration with AI developers is increasingly becoming a key component of prudent strategies for generative AI tool implementation. Working closely with experts allows law firms to raise any queries – and discuss potential issues – while exploring possible AI implementations.
This helps organizations develop team-specific knowledge and familiarity when it comes to understanding how to use an even acutely complex generative AI technology. By forming close partnerships, law firms can access developers’ expertise to further ensure ongoing compliance, responsibility, accountability and accuracy of the systems used.
Through this work conducted one-on-one with developers; legal teams become mindful about addressing risks appropriately throughout every decision making step.
Seeking customized AI solutions that align with the firm’s values
As legal practitioners move forwards with the adoption of generative AI tools amidst various concerns, one way to assure a successful implementation while keeping risks at bay is to collaborate with experienced AI developers already adept in the field.
As a result, firms gain access to customized software that aligns their values and business model closely because of thorough evaluation and testing, leaving room for valuable discussions during problem-solving phases should new challenges arise during program usage.
Ultimately, attentive engagement mitigates worries about irreconcilable deviations of values or interests relative to gaining product efficacy enabled by the firm’s closely hewed working style. Close collaboration ensures success!
Conclusion
Are In summation, AI technology is being increasingly embraced by law firms for professional success on various industry levels. Gaining these potential benefits necessitates care and caution when it comes to forming generative AI implementation plans. Organized steps should be taken to avoid potential errors and biases caused by AI tools, often including evaluations and tests.
Additionally, organizations require assistance tailored to their operations such as HR monitors or procedural review systems to ensure alignment with the legal firm’s values.
Realizing complete benefits comes from pursuing secure incorporation of tools while also making sure risks are minimized through an orderly balance between automation and human management of tech compliments. Prudentities shared today permit successful utilizations of underlying advantages to yield become overly relying advances.