Biotechnology is a branch of science that merges biological concepts with technology for better use and advancements in the field of science, technology, and humanity. Here is biotechnology — the benefits and the risks at a glance.
Biotechnology deploys a range of technologies that use living organisms or a part of them to make all kinds of useful products. These products are as diverse as renewable fuels, drugs, and therapeutics. The products are also as disparate as nutritional compounds, environment-friendly chemicals, and materials, household cleaning products, organs for transplant, and more.
What is Biotechnology?
We can say that biotechnology is the manipulation of living organisms and organic materials in certain different patterns that meet our needs on various platforms. Or simply put, Biotechnology uses living organisms to create useful products.
Biotechnology may have different variations in definitions, but it has a purpose to achieve certain requirements in the field of medicines, agriculture, industries, and more, through manipulations and production.
Let’s check out some of the technical definitions and terminologies of biotechnology as defined by some federations and organizations.
- Defined by the European Federation of Biotechnology – Biotechnology is the application of biochemistry, microbiology and engineering sciences in order to achieve the technological application of the capabilities of microorganisms and cultured tissue cells.
- According to the Biology Industry Organization – Biotechnology is the science of using cellular and biomolecular processes to develop technologies and products.
- According to International Unions of Pure and Applied Chemistry (1981) – biotechnology is the application of biochemistry, biology, and microbiology, chemical engineering to industrial processes, products and on the environment.
The term Biotechnology is often misunderstood.
The OECD — the Organization of Economic Co-operation and Development — defines biotechnology as “the application of scientific and engineering principles to the processing of materials by biological agents.”

Some people have believed the biotechnology is limited to the application of molecular biology techniques to identify genes responsible for particular traits to clone, study, characterize and manipulate, but it is not the case.
There are many rapid advances taking place in different fields of biotechnology like medical biotechnology, agricultural biotechnology, and industrial biotechnology.
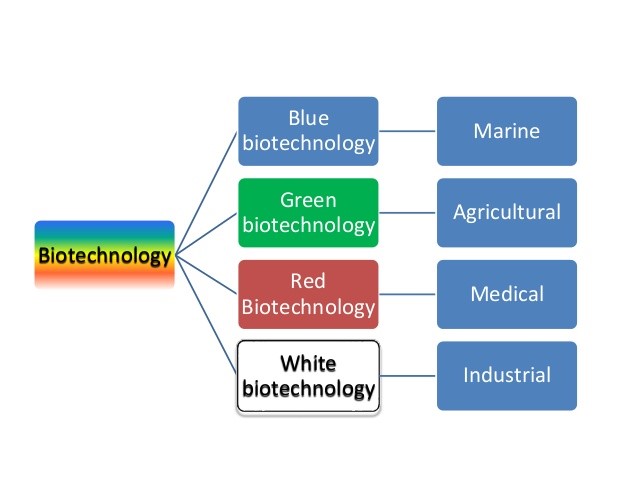
The four major disciplines in biotechnology.
The four major disciplines in biotechnology are medical, industrial, marine and agricultural processes and each process is represented by a specific color. These colors are: red, white, blue, and green respectively.
The four disciplines are known as Red biotechnology, White biotechnology, Blue biotechnology, and Green biotechnology — as per their roles and functions.
- Green biotechnology is used to improve the production quality of crops. Green biotechnology boosts the economy that includes the plant’s tissue culture, engineering culture, and molecular marker-assisted breeding. Green biotechnology is based on providing agricultural solutions without affecting the environment. As it specializes in improving agricultural processes, it has obtained the obtaining of transgenic plants resistant to terrains, and adverse environmental conditions as well as resistant to diseases and pests.
- Red biotechnology is used by biotechnologists to find healthcare solutions. These solutions include vaccines for many dreadful diseases and viruses that currently plague humanity. Also, much research work is done in gene therapy, testing genetics and in the area of “improvement diagnosis.”Red biotechnology is also used for medical processes like obtaining antibiotics, new drugs, vaccines, and newer forms of molecular diagnosis. It has regenerative therapies and the application of genetic engineering to cure diseases.
- White biotechnology is exclusively applied to improve industrial processes. The white biotech will continue producing services and products for industrial and environmental processes. White biotech uses yeast, molds, bacteria, and enzymes for its research. The main aim of white biotechnology is the development of biodegradable products to earn profits and provide better services.
- Blue biotechnology is also known as marine biotechnology. Blue biotechnology is the application of molecular biological methods to marine and freshwater life. It uses marine organisms, and their derivatives, to increase seafood supply. Blue biotechnology increases safety and controls the proliferation of noxious water-borne organisms, and develops new drugs. Blue biotechnology is responsible for the development of aquaculture, care of marine creatures, water treatment and production of food derived from the sea.
Biotechnology and Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is considered the next big thing in biotechnology. Biotechnology is not the only area that artificial intelligence has revolutionized. It’s transformed the research and development activities in many crucial areas.
Almost all the leading biopharmaceutical bigwigs globally are strategically implementing AI-driven technologies in their biotech businesses. AI boost’s up the development processes and gains newer insights in research and development outsourcing.
Artificial intelligence (AI) can be described as the ability of a computer or robot-controlled computer to perform tasks that are commonly associated with intelligent creatures. Specifically, a “scientific discipline that involves building computer systems whose behavior can be interpreted intelligently.

The following are a few of the major applications of AI in biotechnology.
- Diagnostics
- Radiotherapy and Radiology
- Personalized Medicine
- Gene Editing
- Electronic Health Record (EHR)
- Medication Management
- Sales Rep Performance
- Target-based and phenotypic drug discovery
- Polypharmacology discovery
- Biomarkers development
- Analyzing research literature, publications, and patents
Clearly, AI can help identify drug targets, find good molecules from data libraries, suggest chemical modifications, identify candidates for repurposing and so on.
Artificial Intelligence is transforming data into drugs by its amazing technological advances. No wonder all the big pharmacy and biotech are betting big time on AI.
How does Biotechnology impact our lives?
Biotechnology is an innovative, dynamic and ever-evolving cutting-edge sector. It plays a significant role in all major areas of human interests and benefits. Biotech touches all areas including economics, environment, and health. The applications of biotechnology have both positive as well as negative impacts for human civilization.
Biotechnologies are fundamentally oriented for improving the efficiency of production techniques in agricultural, industrial and biomedical fields.
Several advanced surveys and statistics across the globe emphatically explain how biotechnology is poised to change our lives for good.
The “higher purposes” of Biotechnology.
In earlier times, biotechnology’s usage was restricted to fundamental processes like making cheese, wine, bread. Today we have the advantage of superior technologies and the motive of urgent requirements to use biotechnology appropriately for many higher purposes of the society.
Biotechnology is controlling a major part of our lives without us realizing its presence in our surroundings and utilities.
The four disciplines of Biotechnology are in control of our lives.
Controlling many areas, such as the food we eat to medicines we consume, the clothes we wear and how they are washed to the fuel we use, biotechnology is everywhere. The four disciplines of biotechnology are making its invaluable presence felt in meeting our daily needs.
Biotechnology is often being regarded more as an art than a science.
Biotech is sometimes not thought of as a science, but it should be. Because of biotechnology’s ability to touch upon people’s lives by accentuating the quality of life, it’s becoming invaluable.
The solutions Biotechnology provides change results for the grand challenges of society. Solutions are found for food security, climate change, energy shortages, healthcare choices, and affordability. We find solutions for industrial processes and medical needs — even solutions in fighting with epidemics.



















