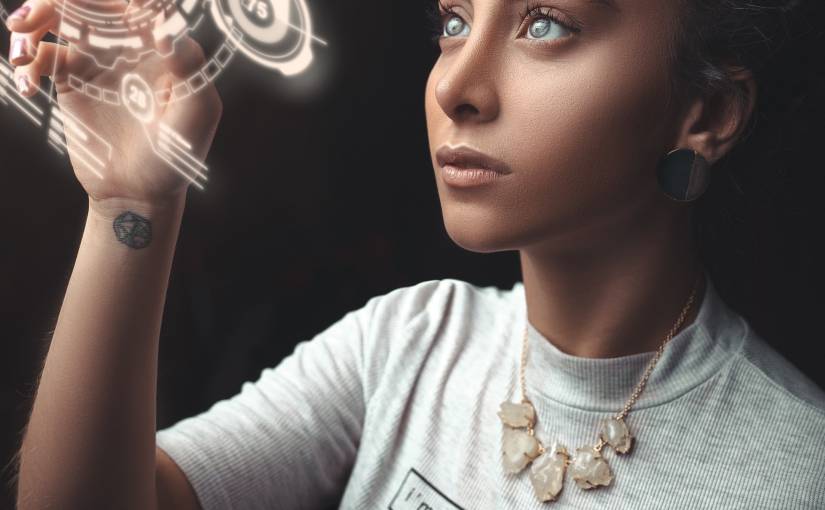
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) tech allow individuals to add computer-generated graphics or informational overlays to the room they’re in. Users can also transport themselves to a completely digital interactive environment.
In the past, technology was limited to academic and research use — and more recently, consumer tech is used in applications like video games and virtual chat platforms.
The massive growth of the VR/AR industry, coupled with rapidly declining hardware prices, has made technology much more accessible. Now, business use of tech is much more common. Developers are working to create new platforms and software that enable VR- and AR-based training in the manufacturing industry.
Here’s how tech works — and how businesses have used VR and AR to make manufacturing training sessions more effective and safer.
How VR and AR Can Transform Training
Augmented reality allows a user to overlay a graphic interface or computer-generated imagery over their real-world environment. A smartphone or similar device is all you need.
Virtual reality is more hardware-intensive. Through the use of a head-mounted display and a high-powered computer, a VR setup can fully transport a user to a digital environment that comes complete with sound, visuals, and — with the right controller — haptic feedback.
The two technologies are sometimes referred to as extended reality, or XR. Both make it possible to overlay additional information on a real-world training setup. They also allow trainers to teach in a completely virtual environment.
Teaching can be extraordinarily valuable for hazardous materials training or factory equipment training. Relevant visuals help make sessions more effective, and training is also less dangerous, since trainees aren’t exposed to a dangerous situation.
Boosting training efficiency is especially important right now as the manufacturing sector faces a labor shortage. With traditional training methods, new workers might not understand their job quickly enough to meet operational demands. Lack of training and understanding can cause stress and lead to more turnovers. By implementing new technologies to optimize training, it can help workers complete training and keep the operation running smoothly.
Key Benefits of VR and AR in Manufacturing Training
Extended reality training can reduce time to competency and improve information retention. Its digital environments can help provide concrete examples or additional context for what a trainee is learning.
Traditionally, machine training is typically only available in analog format or as PDF packets. This may require long periods of study. This can be a significant time investment before the process becomes intuitive. However, extended reality can shorten training time by displaying relevant information and instructions on-screen. It can also highlight parts and draw attention to a system display which can streamline the training process.
Instructors can quickly explain how to use a particular machine. Plus, in many cases, they may be able to do this without requiring trainees to read lengthy training manuals.
Similarly, a VR environment can help make safety training more concrete by providing a trainee with simulations of real-world situations.
This can help make training less abstract and more effective. What if a machine isn’t available for training? With VR, trainees can still learn can how it operates and how to use it. This near hands-on experience can improve learning over text-based training methods. Visual and tactile learners will also be able to grasp concepts quicker.
Several studies and projects have already been conducted on implementing VR and AR in training. Many of them demonstrated that tech could offer advantages over traditional methods.
AR and VR don’t just simplify the training process. There’s also evidence that they may create more effective programs. According to one study from the University of Maryland, the use of immersive head-mounted displays produced a recall of greater than 90% compared to just 78% for desktop-based training.
Boosting retention can speed up the training process and reduce the risk of mistakes due to poor recall. This can also help instructors significantly reduce costs.
Businesses Using VR and AR for Manufacturing Training Right Now
Several businesses in the manufacturing and training industries have already had some key early successes with the technology. These use cases demonstrate how other manufacturers can use the tech and will likely pave the way for new platforms and training tools.
One of the best examples are companies like Strivr, Th3rd Coast, and PIXO VR, which offer VR training as part of their portfolio.
Exact training platform features vary from company to company. Some aim to work with manufacturers to develop training programs based on the machinery and systems they use in their factories. This helps new employees learn how to use equipment in an interactive digital environment. Others create general-purpose training modules that help instructors teach good safety practices.
Existing use cases for this technology include factory hazard identification, lockout/tagout, fall protection, and confined spaces training. These programs help ensure safety once a worker has graduated from training and goes to work on the floor.
Best Practices for Implementing VR- and AR-Based Training
These best practices can help integrate XR technology into training regimens as smoothly as possible.
To start, companies must decide whether they’ll use VR or AR. They must also determine how much to spend on hardware, and which software platforms they’ll use.
Hardware costs may be a barrier to the use of VR technology in a training program. Presently, the cheapest available VR headset, the Oculus 2, retails at around $299. Cheaper VR options are available. Platforms like Google Cardboard, which uses a cardboard shell around a smartphone to create a kind of VR headset, are much cheaper.
AR training may also be a more affordable option. Depending on the particular training technology used, trainees may be able to use an AR platform with their own smartphone. This helps significantly cut down on the training program’s cost.
Once the program is in place, instructors should regularly gather feedback. This will help them adjust how they run future training.
Tracking the right metrics can help trainers identify if a new AR or VR-based program is working well. Plus, it can also help trainers spot any inefficiencies. Many learning and development professionals recommend measuring student engagement, comprehension, and speed to competency.
It’s also good to measure some kind of outcome metric that can show how training has improved the company’s bottom line. It helps to have this concrete information on hand for management and potential clients to see.
As with any new training strategy, business owners should prepare for a phase-in period. Slowly ramping up the use of AR and VR training can provide a sense of how the tech will work in practice. It will also help identify areas a platform may not be able to cover.
Adopting VR and AR Training for Manufacturing Businesses
VR and AR platforms have made it possible for manufacturers to use technology for safety training. VR and AR tech training offers a few key advantages over traditional methods — like improved time to competency and reduced training costs. This has made it appealing to manufacturers wanting to streamline processes in response to a growing industry skills gap. Companies need to get workers up to speed quickly and efficiently, and XR fits the bill.
Businesses wanting to adopt VR or AR training tech should focus on best practices to get the most out of their sessions. Careful choice of platform, measuring the right training metrics, and prepping for a phase-in period can ensure the training process’s adoption goes smoothly. This type of training will ensure employees learn their duties thoroughly and can do their jobs with confidence, boosting productivity and helping manufacturers stay ahead of the curve.
Image Credit: ali pazani; pexels