I’m in Santa Clara, California this week attending (and speaking) at the Augmented Reality Event – a conference focused on the business of AR that has experts from across the world gathered to share their ideas. While at the event, my goal has been to hunt down innovative and unique real-world practical applications for augmented reality in order to shed light on the usefulness of the technology. According to Dr. Michael Aratow, augmented reality is playing a huge role in the medical field, and some of his examples of medical AR were fascinating.

According to Aratow, Chief Information Officer for San Mateo Health Services, AR has been used in the medical field for nearly ten years. For a long time, AR lived on high-tech levels, and producing products that leveraged it required advanced computing technology only available to large corporations. This is why a lot of early AR development existed in large manufacturing companies, such as auto and aircraft makers. Medical manufacturers have also dipped into AR, but thanks to funding from the Recovery Act, far further research and development for medical AR tools has been made possible.
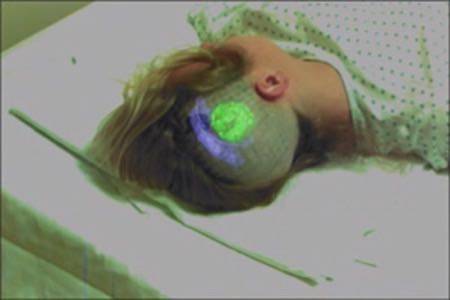
One of the interesting uses for AR in the medical field involves live interactive imaging for assisting physicians, medical students and children. Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) includes procedures where a camera is inserted into the patient’s body to help the doctor visualize the procedures he or she is conducting. In one example, this form of surgery is aided with the use of AR imagery of a brain superimposed onto the patient’s head, giving the doctor a more tangible visualization. Another example involves being able to visualize a patient’s spine in order to more accurately place a spinal tap, or other spinal injection.
These visualizations can also extremely useful tools for educating both students and children about medicine. With the help of augmented reality projections of bones, muscles, nerves and other internal body parts, med students can practice procedures on mannequins in a somewhat real-world game of “Operation.” Applications can also help teach kids about anatomy by allowing them to peer under the skin and reveal the inner workings of human bodies.
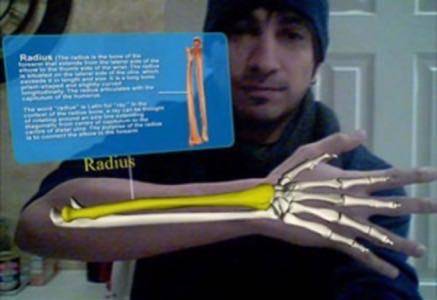
Other possibilities for media AR applications lie in leveraging and managing the massive mine of patient data. Imagine, for example, that in order to check a patient’s history, the doctor would need only to look the patient over while wearing a head-mounted display (HMD). Virtual tags could appear on the patient to locate previous injuries or illnesses and provide valuable data to the doctor instantly and in context with the patient.
HMDs are also where some the limitations of media AR applications exist. According to Christopher Stapelton, founding director of the Media Convergence Laboratory at the University of Central Florida, there are significant hurdles to overcome when integrating HMDs with medical devices. Among these are common HMD issues, such as accurately placing and applying depth perception to 3D models, as well as medical specific problems, like allowing doctors to see the tools they are holding through the projected image.
Stapelton showed off some amazing videos of devices scanning a human head and showing bone structure through a face. Even with the face moving and creating expressions, the bones were visible in their appropriate locations in the area which the device was scanning. When an instrument (in this case, a spoon), was held in front of the area being scanned, the data was removed for that area, and real-time shadows from the instrument were placed on the imagery.
These stunning examples are just a few of the ways AR is influencing the medical industry. There are several other areas in which augmented reality is having a significant impact with a practical use – a quality I believe is imperative to the future success of the technology.





















