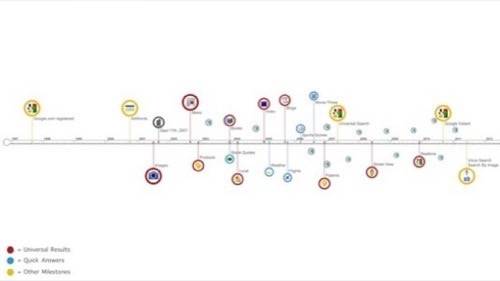
As the year winds down, Google has released some introspective blog posts about its changing nature. Today, it recapped the evolution of search in six minutes, describing the evolution of Google’s core product from its breakout PageRank algorithm to its new real-time, local and social directions. It also published an illuminating timeline of the major changes to Google search.

Last week, Google fellow Amit Singhal, who appears in today’s video, published some thoughts on personalization, which has been Google’s most publicized and controversial change to its core product. Google’s in a thoughtful mood about its recent changes. As Vic Gundotra made clear at Web 2.0 this fall, the company’s whole identity is shifting. Here are four major trends in how Google search has evolved over time.
Universal Search
Google’s introduction of universal search in 2007 was the beginning of a trend away from separating Web search results by type and toward putting it all in one place. As connection speeds improved and video and image content became ubiquitous, Google found that different types of results could still be relevant to one query. Soon enough, Google users began to find videos, images and place results all in response to one search.
But as Google got better at indexing these varied kinds of content, it also expanded its portfolio of Web services into dedicated tools for organizing and presenting them. By acquiring YouTube and building out dedicated Web properties for News, Maps, Places, Shopping and more, Google began to advance its search-based advertising business into the realms of its competitors, including content companies.
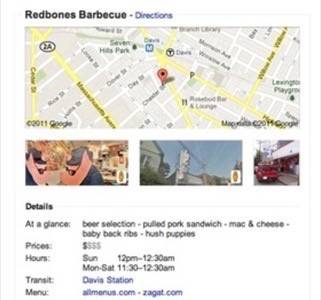
Google Goes Mobile & Local
Before long, Google was deep into the business of local commerce. With the rise of Android, Google had an end-to-end business of finding location-based results for local businesses, restaurants and destinations. It began to build commerce businesses like daily deals and mobile payments to monetize it. And local business offered a rich vein of advertising dollars, so Google made the mobile Web, and mobile ads, a top priority.
Google’s local efforts played right into universal search by making maps and place results more relevant, even when a user searched from his or her desktop. This inevitably led to clashes with competitors like Yelp, whose dedicated local business content was threatened by Google’s integration. But Google kept going, even acquiring professional local business content company Zagat. Google’s definition of relevance grew broader.
Google Search and Time
Google has changed the impact of time on search, as well as place. It has tweaked the way timeliness of content appears in search multiple times, and its latest update calculates when a search is probably looking for recent results rather than historical ones.
At the same time, Google has eliminated some historical features from search, shifting the priority onto real-time results. Now that Google’s users are out and about using Google to find things to do, it has to respond in real time.
Google+: Google’s New Identity
Identity is the final piece of the puzzle. Google has personalized results for a while using Web history and sharing data. But with the launch of Google+, Google has introduced a form of social SEO. Social activity is now a fundamental part of how search results appear for users logged into Google’s ubiquitous Web services.
The +1 button is all over the place now, and Google is using this signal to determine which results to show its users by analyzing their interests. As Singhal said in his thoughts on personalization, it’s all about context. Google can better figure out what a query means to its users if it has real-time and social signals.

At Web 2.0, Gundotra said that Google had shipped the “Plus part,” meaning the social network itself, and is now shipping “the Google part,” meaning the way Google+ signals integrate with relevance in search. The “+” is a small modifier to the name “Google,” but it represents a whole new understanding of what constitutes meaning in Web search.
Check out the six-minute video of Google’s “Evolution of Search:”










